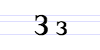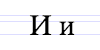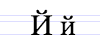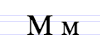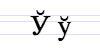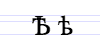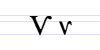User:Mzajac/cyrillic
Not to be used as a reference. This page is my own work in progress. Some parts are just placeholders, or incomplete, while others have already been entered into other WP articles and further revised there.
[edit]
Simple navigation table. Title attributes serve as English labels. Letters ordered according to Unicode correlation tables. Currently at Template:Cyrillic alphabet navbox.
The template would be inserted with code like the following. Parameters insert the heading and link to the image.
{{Template:Cyrillic alphabet navbox|
Heading=Cyrillic letter A|
Image=Image:Cyrillic letter A.png
}}
Letter images[edit]
National alphabets[edit]
Slavic[edit]
Belarusian[edit]
From Belarusian language.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | І і | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ў ў |
| Ф ф | Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
- Г is called "He", pronounced /ɦ/.
- І is called "I", pronounced /i/.
- Ў is called "short U", pronounced /w/.
- An apostrophe negates palatalization.
Before 1933, Ґ (/g/) was also present. Some linguists call for restoring the letter.
Belarusian is also written in Łacinka, a Latin alphabet.
Bulgarian[edit]
From Bulgarian language.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й | К к |
| Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф | Х х |
| Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ь ь | Ю ю | Я я |
- Е is called "E", pronounced /e/.
- Щ is called "Shta", pronounced /ʃt/.
- Ъ is a vowel /ə/.
Macedonian[edit]
From Macedonian language.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Ѓ ѓ | Е е | Ж ж | З з | Ѕ ѕ | И и |
| Ј ј | К к | Л л | Љ љ | М м | Н н | Њ њ | О о | П п | С с | Ќ ќ |
| У у | Ф ф | Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Џ џ | Ш ш |
- Е is called "E", pronounced /e/.
- Ѕ is called "Dze", pronounced /dz/.
- Ѓ is called "Gje", pronounced /gj/
- Ј is called "Ej", pronounced /j/
- Љ is called "Lj", pronounced /lj/
- Њ is called "Nj", pronounced /nj/
- Ќ is called "Kja", pronounced /kj/
- Џ is called "Dzh", pronounced /dʒ/
Russian[edit]
From Cyrillic alphabet.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
With links
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Serbian[edit]
From Serbo-Croatian language.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Ђ ђ | Е е | Ж ж | З з | И и | Ј ј |
| К к | Л л | Љ љ | М м | Н н | Њ њ | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т |
| Ћ ћ | У у | Ф ф | Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Џ џ | Ш ш |
- Е is called "E", pronounced /e/.
- Ђ is called "Djerv", pronounced /dj/
- Ј is called "Ej", pronounced /j/
- Љ is called "Lj", pronounced /lj/
- Њ is called "Nj", pronounced /nj/
- Ћ is called "Tjerv", pronounced /tj/
- Џ is called "Dzh", pronounced /dʒ/
Serbian can also be written in the Latin alphabet.
Ukrainian[edit]
From Ukrainian alphabet.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Ґ ґ | Д д | Е е | Є є | Ж ж | З з | И и |
| І і | Ї ї | Й й | К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с |
| Т т | У у | Ф ф | Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ю ю | Я я | Ь ь |
- Г is called "He", pronounced /ɦ/.
- Ґ is called "Ge", pronounced /g/. This letter was not officially used in the Soviet Union, so it is missing from some Cyrillic fonts.
- Е is called "E", pronounced /e/.
- Є is called "Ye", pronounced /je/.
- И is called "Y", pronounced /ɪ/.
- І is called "I", pronounced /i/.
- Ї is called "Yi", pronounced /ji/.
- Й is called "Yot", pronounced /j/.
- An apostrophe negates palatalization.
Modern Church Slavonic[edit]
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Old Church Slavonic[edit]
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Є є | Ж ж | Ѕ ѕ | З з | І і | И и |
| Ћ ћ | К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | Ѹ ѹ |
| Ф ф | Ѳ ѳ | Х х | Ѡ ѡ | Щ щ | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Ъ ъ | ЪІ ъі | Ь ь |
| Ҍ ҍ | Ю ю | Я я | Ѧ ѧ | Ѫ ѫ | Ѩ ѩ | Ѭ ѭ | Ѯ ѯ | Ѱ ѱ | Ѵ ѵ |
Я was written in an archaic form called A iotified.
Source: Old Church Slavonic Online, Linguistics Research Center, The University of Texas at Austin
Non-Slavic[edit]
Abkhaz[edit]
Abkhaz is a Caucasian language, spoken in the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia, Georgia. See Abkhaz alphabet.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Гь гь | Ҕҕ | Ҕь ҕь | Д д | Дә дә | Џ џ | Џь џь |
| Е е | Ҽ ҽ | Ҿ ҿ | Ж ж | Жь жь | Жә жә | З з | Ӡ ӡ | Ӡә ӡә | И и | Й й |
| К к | Кь кь | Қ қ | Қь қь | Ҟ ҟ | Ҟь ҟь | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | Ҩ ҩ |
| П п | Ҧ ҧ | Р р | С с | Т т | Тә тә | Ҭ ҭ | Ҭә ҭә | У у | Ф ф | Х х |
| Хь хь | Ҳ ҳ | Ҳә ҳә | Ц ц | Цә цә | Ҵ ҵ | Ҵә ҵә | Ч ч | Ҷ ҷ | Ш ш | Шь шь |
| Шә шә | Щ щ | Ы ы |
Altay[edit]
Altay is spoken in the Altai Republic of Russia.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Avar[edit]
Avar is spoken in southern Dagestan and parts of Azerbaijan. It also uses a modified Arabic script called Ajam. See Avar language.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Azerbaijani[edit]
Officially, Azerbaijan now uses a Latin alphabet, but the Soviet-era Cyrillic alphabet is still in wide use. Azerbaijani language speakers in Iran use the Arabic alphabet.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Chukchi[edit]
Chukchi is spoken mainly in the region of Chukotka, in easternmost Siberia.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Chuvash[edit]
Chuvash is spoken in the Russian Republic of Chuvashia. See Chuvash language.
| А а | Ӑ ӑ | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ӗ ӗ | Ж ж | З з |
| И и | Й й | К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Ҫ ҫ |
| Т т | У у | Ӳ ӳ | Ф ф | Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы |
| Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Dungan[edit]
Dungan, spoken in Kyrgyzstan, is the only variation of Chinese language that is not normally written in Chinese characters.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Erzya[edit]
Erzya, Moksha and Russian are official languages of Mordovia. See Erzya language.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Kazakh[edit]
Kazakh, spoken in Kazakhstan, can also be written using modified Latin (in Turkey) or Arabic (in China, Iran, and Afghanistan) alphabets.
| А а | Ә ә | Б б | В в | Г г | Ғ ғ | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з |
| И и | Й й | К к | Қ қ | Л л | М м | Н н | Ң ң | О о | П п | Ө ө |
| Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ұ ұ | Ү ү | Ф ф | Х х | Һ һ | Ц ц | Ч ч |
| Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | İ і | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Kildin Sami[edit]
Kildin Sami is spoken in the Kola Peninsula in northwestern Russia.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Komi[edit]
Komi-Zyrian[edit]
Komi-Zyrian language is spoken in the Komi Republic of Russia.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Komi-Permyak[edit]
Komi-Permyak is spoken in the Autonomous district of the Komi-Permyaks.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Kyrgyz[edit]
The Kyrgyz language of Kyrgyzstan uses Cyrillic. In China it is written in modified Arabic. There is also an official Latin which is enjoying official endorsement again, but actual use is sporadic and inconsistent
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Mongolian[edit]
Mongolian is mostly written in Cyrillic, but the traditional Mongolian alphabet is slowly being reintroduced in the public schools.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Ossetic[edit]
Ossetic language is spoken in North Ossetia-Alania, Russia, and in South Ossetia, Georgia. Ossetian may be immediately recognized by its unique use of the ? among Cyrillic alphabets.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Tatar[edit]
Kazan Tatar is also written in a Latin alphabet, which is replacing the Cyrillic. See Tatar alphabet. Crimean Tatar language has its own alphabet derived from the Turkish.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Keräşen Tatar[edit]
Keräşen Tatars, mainly from Tatarstan, use their own Cyrillic alphabet.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Tuvan[edit]
Tuvan is spoken in the Russian Republic of Tuva, in south-central Siberia.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Udmurt[edit]
Udmurt is spoken in the Russian Republic of Udmurtia.
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Yakut[edit]
Yakut is spoken mainly in the Russian Repiblic of Sakha (Yakutia).
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж | З з | И и | Й й |
| К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф |
| Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э | Ю ю | Я я |
Glagolitic[edit]
Punctuation (source: [1]):
- , 002C COMMA
- . 002E FULL STOP
- ; 037E (GREEK QUESTION MARK)
- · 0387 GREEK ANO TELEIA (semicolon equivalent)
- : 0589 ARMENIAN FULL STOP
- :· 10FB GEORGIAN PARAGRAPH SEPARATOR
- ·: 2056 TRIANGULAR COLON
- ·:· 2058 DIAMONDCOLON
- :·: 2059 QUINTUPLECOLON
Early Cyrillic alphabet[edit]