Regular semantics
This article's tone or style may not reflect the encyclopedic tone used on Wikipedia. (May 2023) |
Regular semantics is a computer hardware consistency model. It describes a type of guarantee provided by a processor register that is shared by several processors in a parallel machine or in a network of computers working together. Regular semantics are defined for a variable with a single writer but multiple readers. These semantics are stronger than safe semantics but weaker than atomic semantics: they guarantee that there is a total order to the write operations consistent with real-time and that read operations return either the value of the last write completed before the read begins, or that of one of the writes which are concurrent with the read.
Example[edit]
Regular semantics are weaker than linearizability. Consider the example shown below, where the horizontal axis represents time, and the arrows represent the interval during which a read or write operation takes place. According to a regular register's definition, the third read should return 3 since the read operation is not concurrent with any write operation. On the other hand, the second read may return 2 or 3, and the first read may return either 5 or 2. The first read could return 3 and the second read could return 2. This behavior would not satisfy atomic semantics. Therefore, regular semantics is a weaker property than an atomic semantics. On the other hand, Leslie Lamport proved that a linearizable register may be implemented from registers with safe semantics, which are weaker than regular registers.[1]

A Theorem from Regularity to Atomicity[edit]
This article may be confusing or unclear to readers. (January 2015) |
A single-writer multi-reader (SWMR) atomic semantics is an SWMR regular register if any of its execution history H satisfies the following property: r1 and r2 are any two read invocations: (r1 →H r2) ⇒ ¬π(r2) →H π(r1)
Before getting into the proof, first, it should be understood what the new/old inversion means. As it shown in the picture below, by looking at the execution it can be seen that the only difference between a regular execution and an atomic execution is when a = 0 and b = 1.In this execution, when considering the two read invocations R.read() → a followed by R.read() → b, our first value (new value) is a = 0 while the second value (old value) is b=1. This is actually the main difference between atomicity and regularity.
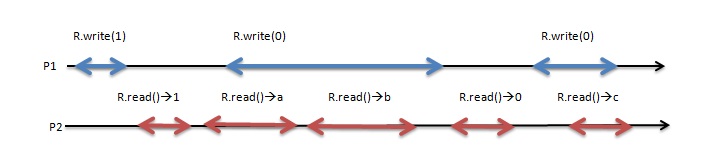
The theorem above states that a Single writer multi-reader regular register without new or old inversion is an atomic register. From it, R.read() → a →H R.read() → b and R.write(1) →H R.write(0), it is not possible to have π (R.read() → b) =R.write(1) and π (R.read() → a) = R.write(0) if the execution is atomic. To prove the theorem above, first it must be proven that the register is safe, regular and that it does not allow for new/old inversion which proves the atomicity. By the definition of the atomic register, a Single writer multiple reader atomic register is regular and satisfies the no new/old inversion property. So, the only required proof is to show that a regular register with no new/old inversion is atomic.
Moreover, for any two read invocations (r1 and r2) when the register is regular and there is no new/old inversion (r1 →H r2) ⇒sn(π(r1)) ≤ sn(π(r2)). For any execution (M) there is a total order (S) which includes the same operation invocations. It can be stated that S is built as follow: starting from the total order on the write operations and the read operations being inserted as follow: first: Read operation (r) is inserted after the associated write operation (π(r)). Second: If two read operations (r1,r2) have the same (sn(r1)=sn(r2)) then first insert the operation which starts first in the execution. S includes all the operation invocation of M, from which it follows that S and M are equivalent. Since all the operations are ordered based on their sequence numbers is slightly a total order. Furthermore, this total order is an execution of M only adds an order on operations that are overlapping in M. If there is no overlapping between a read and write operations, there is no difference between the regularity and atomicity. Finally, it can be stated that S is legal since each read operation gets the last written value that comes before it in the total order. Therefore, the corresponding history is linearizable. Since this reasoning does not rely on a particular history H, it implies that the register is atomic. Since atomicity (linearizability) is a local property, it can stated that a set of SWMR regular registers behave atomically as soon as each of them satisfies the no new/old inversion property.
References[edit]
- ^ Lamport, Leslie (1986). "On interprocess communication - Part I: Basic formalism". Distributed Computing. Springer-Verlag. doi:10.1007/BF01786228.
- Lamport, Leslie "On Interprocess Communication" http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/lamport/pubs/interprocess.pdf (1986)
