Cat's cradle
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2017) |
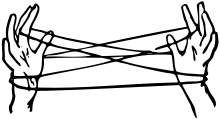
Cat's cradle is a game involving the creation of various string figures between the fingers, either individually or by passing a loop of string back and forth between two or more players. The true origin of the name is debated, though the first known reference is in The light of nature pursued by Abraham Tucker in 1768.[1] The type of string, the specific figures, their order, and the names of the figures vary. Independent versions of this game have been found in indigenous cultures throughout the world, including in Africa, Eastern Asia, the Pacific Islands, Australia, the Americas, and the Arctic.[2]: page 161 [3][4]
Play[edit]

The simplest version of the game involves a player using a long string loop to make a complex figure using their fingers and hands.[5]
Another version of the game consists of two or more players making a sequence of string figures, each altering the figure made by the previous player. The game begins with one player making the eponymous figure Cat's Cradle (above). After each figure, the next player manipulates that figure and removes the string figure from the hands of the previous player with one of a few simple motions and tightens the loop to create another figure, for example, Diamonds. Diamonds might then lead to Candles (which is also known as Pinkies), for example, and then Manger—an inverted Cat's Cradle—and so on. Most of the core figures allow a choice between two or more subsequent figures: for example, Fish in a Dish can become Cat's Eye or Manger. The game ends when a player makes a mistake or creates a dead-end figure, which cannot be turned into anything else.[6] Many players believe that Two Crowns or King's Crown is one such dead-end figure, although more experienced players recognize that it can be creatively maneuvered into Candles or Pinkies, which allows the game to continue.
History[edit]

The origin of the name "cat's cradle" is debated but the first known reference is in The light of nature pursued by Abraham Tucker in 1768.[1]
"An ingenious play they call cat's cradle; one ties the two ends of a packthread together, and then winds it about his fingers, another with both hands takes it off perhaps in the shape of a gridiron, the first takes it from him again in another form, and so on alternately changing the packthread into a multitude of figures whose names I forget, it being so many years since I played at it myself."[1]
The name may have come from a corruption of cratch-cradle, or manger cradle[nb 1][nb 2] (although this derivation is disputed by the OED). The connection between the two words, cratches and cradle, may come from the Christian story of the birth of Jesus, in which a manger is used as a cradle.[7][8]
In an 1858 Punch cartoon[9] it is referred to as "scratch cradle", a name supported by Brewer's 1898 Dictionary.[10] As "Cat's cradle" often is used to refer to string figures and games in general, Jayne uses "Real Cat's-Cradle" to refer to the specific game.[11]
Different cultures have different names for the game, and often different names for the individual figures. The French word for manger is crèche, and cattle feed racks are still known as cratches. In Japan it is called “ayatori.” In Korea it is called "sil-tteu-gi." In Russia the whole game is called simply, the game of string, and the diamonds pattern is called carpet, with other pattern names such as field, fish, and sawhorse for the other figures—a cat isn't mentioned.[12] The game may have originated in China.[citation needed][13] In China the game is called 翻繩 fan sheng (English: turning rope),[11][12] In Israel the game is called "Knitting Grandmother" (in Hebrew: "סבתא סורגת", Savta Soreget). In some regions of the U.S., this game also is known as Jack in the Pulpit.[14]
World records[edit]
Geneva Hultenius, Maryann Divona, and Rita Divona completed 21,200 changes of cat's cradles in 21 hours in Chula Vista, California between August 17–18, 1974. The Guinness Book of World Records reported it as a world record in the 1975 and 1976 editions.[15]
Jane Muir and Robyn Lawrick completed 22,700 changes of cat's cradles in 21 hours at Calgary Market Mall, Alberta, Canada on August 25, 1976.[16]
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ "Nares, under Cratche, an archaic word for manger, deems it to be the origin of the name of this game, which, however, he calls scratch-cradle. But it clearly, he says, meant originally cratch-cradle, the manger which held the Holy Infant as a cradle..."[7]
- ^ "This opens to us the meaning of a childish game, corruptly called scratch-cradle, which consists in winding a packthread double round the hands, into a rude representation of a manger, which is taken off by the other player on his hands, so as to assume a new form, and thus alternately for several times, always changing the appearance. The art consists in making the right changes. But it clearly meant originally the cratch-cradle; the manger that held the Holy Infant as a cradle."[8]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Martin, Gary. "'Cat's Cradle' - the meaning and origin of this phrase". Phrasefinder. Retrieved 2018-01-16.
- ^ Henry B. Collins (1964) [First published 1888]. introduction. The Central Eskimo. By Boas, Franz. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 0-8032-5016-9.
- ^ Zgheib, Yara (2017-12-21). "Cat's Cradle". Huffington Post. Retrieved 2018-01-16.
- ^ Archives, National Anthropological (2010-05-13). "Cat's Cradle". Smithsonian Collections Blog. Retrieved 2018-01-16.
- ^ Gryski, Camilla (1985). Many Stars & More String Games, pp. 66–72. Tom Sankey, illustrator. ISBN 0-688-05792-6.
- ^ Gryski, Camilla (1984). Cat's Cradle, Owl's Eyes: A Book of String Games. Tom Sankey, illustrator. ISBN 0688039413.
- ^ a b Taylor, E.S. "Cats-Cradle", pp. 412–422 of Notes and Queries: A Medium of Inter-communication for Literary Men, Artists, Antiquaries, Genealogists, Etc., pp. 421–422, Vol. 11 (January—June, 1855). London: George Bell (1855).
- ^ a b Nares, Robert. A Glossary: Or, Collection of Words, Phrases, Names, and Allusions to Customs, Proverbs, Etc., p. 203. London: Gibbings and Company, Limited (1901).
- ^ "Snowed Up", John-Leech-Archive.org.UK.
- ^ "Scratch Cradle", Bartleby.com.
- ^ a b Jayne, C. F. (1906). String Figures and How to Make Them. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. p. 324. ISBN 978-0-486-20152-8.
- ^ a b Buchanan, Andrea J. and Peskowitz, Miriam (2007). The Daring Book for Girls, p.277. ISBN 978-0-06-147257-2.
- ^ (1989). Anthroquest: the L.S.B. Leakey Foundation news, Issues 39–46, p.17. The Foundation.
- ^ Anderson, John P. (2010). Joyce's Finnegans Wake: The Curse of Kabbalah, Volume 4, p.301. ISBN 978-1-59942-810-9.
- ^ McWhirter, Norris and McWhirter, Alan Ross (1975). Guinness Book of World Records, 1976, p.459. Revised. ISBN 978-0-8069-0014-8.
- ^ McWhirter, Ross (1983). Guinness Book of World Records 1979, p.453. ISBN 978-0-8069-0130-5.
External links[edit]
- "Directions for play by C.F. Jayne", a digital version of C.F. Jayne's 1906 compendium, featuring many other string figures.
- "Directions for play at Alysion.org"
- "Directions for play at IfYouLoveToRead.com"
- "Directions for play at wikihow.com", a high-bandwidth page with videos for each of the different steps of the game.
- How to do Cat's Cradle, MomsMinivan, video, August 7, 2013, with a link to written instructions.

